Delve into the intricate world of metal stamping, exploring the step-by-step process of transforming metal sheets into precision components. How does a simple metal sheet evolve into a meticulously crafted part? Let's uncover the production cycle of metal stamping.
The metal stamping production cycle is a systematic process that includes several stages from the initial design and material selection to the final stamped product. This cycle ensures that every metal part produced has the highest precision, consistency, and quality.
Let's delve deeper into each stage of the metal stamping production cycle, revealing the complexity, technology, and craftsmanship that form this fascinating manufacturing process.
Introduction to Metal Stamping
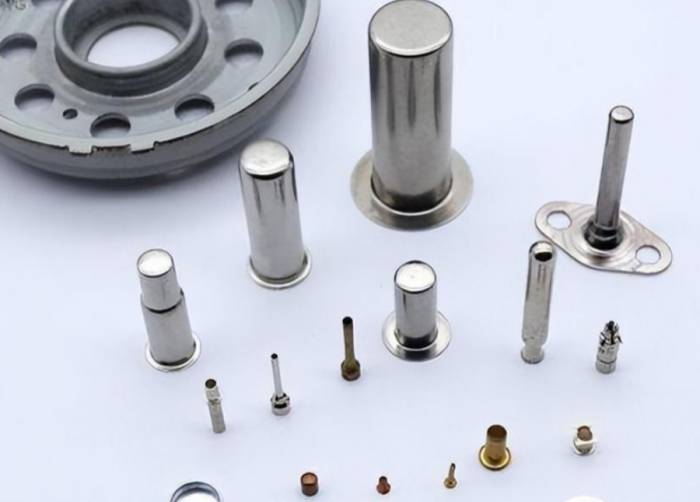
Metal stamping is a cornerstone of the manufacturing industry, a process that transforms flat metal sheets into specific shapes. This technology has a history spanning centuries, evolving with technological advancements to meet the dynamic demands of various industries. From the automotive sector to electronics, the footprint of metal stamping is ubiquitous, highlighting its key role in producing countless components that drive the modern world.
The production cycle of metal stamping is not just about the transformation of metal sheets but a meticulous process that ensures precision, consistency, and quality. A well-defined production cycle is crucial as it determines the efficiency of the process, the quality of the output, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the operation.
The Essence of Metal Stamping
So, what exactly is metal stamping? At its core, metal stamping is a cold forming process that uses dies and punches to shape metal sheets. When the punch is activated and pushes the metal into the die cavity, the metal sandwiched between the die and punch takes shape and is processed into the desired form.
The role of dies and machinery in this process cannot be overstated. Custom-made dies for each project determine the shape, size, and features of the stamped parts. They come in various types, ranging from simple to complex, to meet a wide array of application needs. The machinery, on the other hand, provides the necessary force to ensure the metal conforms to the die's design. Together, they form the heart and soul of the metal stamping process, ensuring that each stamped part meets the precise specifications and standards set by the industry.The Various Stages of the Metal Stamping Production Cycle
The metal stamping production cycle is a series of meticulously planned steps that ensure each metal component is precise, consistent, and efficient. Let's delve into the various stages of this transformative journey.
Design and Prototyping
Before any metal is formed, the entire process begins with conception. This conceptual phase includes envisioning the final product, understanding its functionality, and determining its specifications. Once the concept is clear, prototypes can be made. These are preliminary versions of the product that allow manufacturers to test and refine their design. Prototyping is crucial as it provides insights into potential flaws, areas for improvement, and the feasibility of the design in the real world.
Material Selection
The choice of metal plays a significant role in the stamping process. Different metals have different characteristics, and the selection often depends on the intended use of the stamped part. Factors such as strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and cost influence this decision. For instance, the automotive industry may prioritize strength and durability, while the electronics industry might lean towards metals with good electrical conductivity.
Die Development
The die is the heart of the stamping process. It is a custom tool that imparts shape to the metal. The design of the die requires complex planning to ensure it aligns perfectly with the product specifications. Once the design is finalized, the die is manufactured, typically using high-grade steel to withstand the stamping pressures. Before being put into service, the die undergoes rigorous testing to ensure the precision and quality of the stamping process.
The Actual Stamping Process
This is where the metal is actually formed into the desired shape using the die. The process involves placing the metal sheet between the die and a punch, which is then pressed with a stamping press. The pressure forces the metal to conform to the shape of the die, creating the final part. This stage requires precise control of force and speed to achieve the desired outcome without damaging the part or the die.Once the molds are ready, the actual stamping process begins. The metal sheet is fed into the press, where it meets the mold. Using a powerful press, the metal undergoes operations such as punching, bending, and embossing. Punching is for creating holes, bending is to angle the metal to a certain degree, and embossing is for imprinting patterns. Each operation is carried out with precision to ensure the metal takes the desired shape.
Post-Stamping Operations
After the metal stamping is completed, the process is not yet over. The stamped parts usually undergo trimming to remove excess material. If necessary, further shaping is done, and surface treatments are applied to enhance their appearance and corrosion resistance. Finally, each component is subjected to quality inspection and testing. This ensures that each part meets established standards and is ready for use.
Technological Advances in Metal Stamping
In an era where technology is reshaping industries, metal stamping is no exception. While traditional methods were effective, they have now been replaced by cutting-edge technologies that ensure greater precision, efficiency, and adaptability. Let's explore how these technological marvels are redefining the field of metal stamping.
Automation in Metal Stamping
Automation has changed the game in manufacturing, and the metal stamping industry has wholeheartedly embraced it. Automated stamping presses, feeders, and transfer systems make the production process faster and more stable. Automation reduces manual intervention, thereby reducing errors and increasing productivity. Additionally, automation allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments to ensure that each stamped part meets the highest quality standards.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence is not just a buzzword; it is a transformative force in the field of metal stamping. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, stamping equipment can now predict and prevent potential issues before they arise. For instance, AI can analyze patterns in the stamping process and detect anomalies, allowing for timely intervention. Moreover, AI-driven predictive maintenance can forecast when machinery or molds will need servicing, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous production.The Prospects of Emerging Technologies
Beyond automation and artificial intelligence, the emergence of other technologies also brings boundless hope for the future. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies will completely transform design and prototyping, allowing engineers to visualize and test designs in virtual space before actual production. Furthermore, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) means that machines are more interconnected than ever, enabling seamless data exchange, remote monitoring, and process optimization.
Conclusion
Metal stamping is a craft that has been honed over centuries, a testament to human ingenuity and relentless pursuit of precision. As we navigate its intricate production cycle, we find that every stage from design to post-press operations is a harmonious union of art and science. This meticulous process ensures that every metal component produced not only meets but often exceeds expectations.
However, like all crafts, metal stamping is not static. It is evolving, adapting, and growing. The application of modern technology to this ancient craft clearly demonstrates its dynamic nature. Automation, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies have not only improved the level of craftsmanship but also laid the foundation for a new era of metal stamping. This is an era where precision and efficiency coexist with tradition and innovation.
As we stand on the cusp of this exciting future, one thing remains certain: metal stamping will continue to play a key role in shaping the world around us. In this process, metal stamping will continue to break boundaries, embrace innovation, and set new standards of excellence. The future of metal stamping is not just about shaping metal but about shaping possibilities. In this journey, the best is yet to come.


























Join the Conversation